SMEMACH:Austempered Ductile Iron
Hi everyone, I am SME. Today, let’s talk about some great things that happen in steel when it is heated, two magical form appears, Austenite and Martensite.
Martensite and austenite have their own advantages, the advantages and disadvantages of martensite and austenite should be judged from different application occasions and performance requirements.
Martensite is usually the main one when the temperature is drastically lower than 400℃ The key is that the cooling has to cool quickly enough, that’s quenching.
The generation of austenite happens in high temp more than 727℃ and the creation of austenite needs a certain amount of insulation time to let carbon atoms completely diffuse and spread out equally in the γ-Fe.
The factory needs to have some corresponding equipment, and technical masters, and it also needs the control of the process.
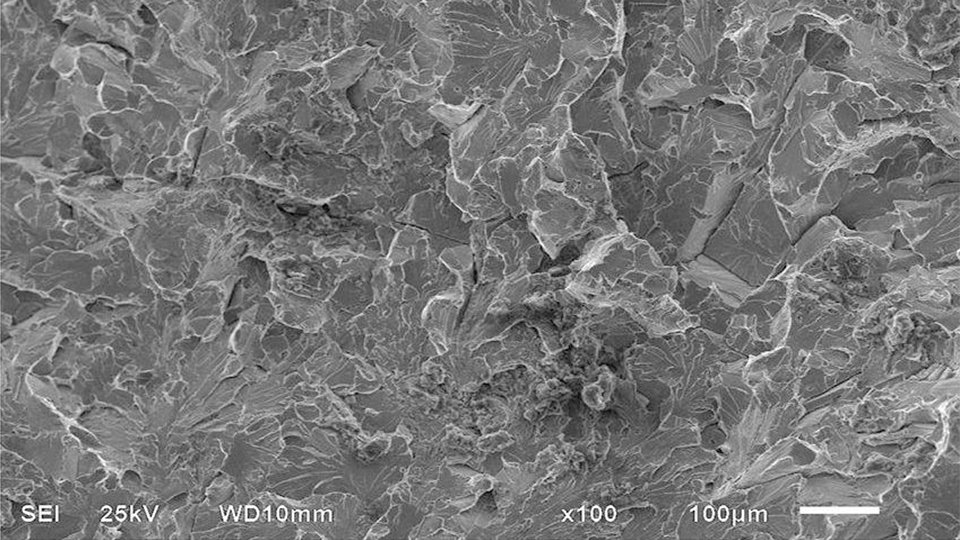
Performance characteristics of martensite: Martensite is very hard and strong The tensile strength of the metal reached over 1000MP, the yield strength was around 800MP, and the hardness was over HRC50 after quenching and other heat treatment process.
Because martensite is hard and strong, but less tough and plastic, it tends to easily break brittle.
It is magnetic, and it become more and more magnetic with the increase of carbon.
Performance characteristics of austenite: Austenite is good at plasticity and toughness. The austenitic stainless steel can achieve an elongation of 40%~60% during cold processing, and it can withstand great deformation without breaking.
Also, austenite is generally non-magnetic or slightly magnetic, so it is mostly suitable for applications with special magnetic requirements.
Application fields of martensite: Martensite has both high hardness and high strength, so it is suitable for use as a tool material. In cold working die and hot working die, martensite structure also can not be ignored. The cold work die must take rather great pressure and friction. Martensitic structure is hard enough to do so, while hot working dies are in a high temperature working environment. After proper tempering martensite still has some hardness with better thermal stability and fatigue resistance.
For some mechanical parts with high surface hardness and high internal toughness requirements, such as shaft parts, gears, etc., surface quenching and other ways to form parts surface is martensite structure, improve parts wear and fatigue resistance, to maintain a certain toughness inside.
Application of austenite: Among all types of stainless steels, austenitic stainless steel is the most commonly used. It’s got decent amount of alloying stuff such as chromium and nickel. It has an austenitic structure at room temperature. It is corrosion-resistant and has good plasticity and toughness. and many times can be found in food production equipment, medical equipment, construction decoration material, etc.
At the same time, in the hot forging and rolling process, the metal is heated into the austenite region, so that the metal has good plasticity, which is conducive to plastic deformation processing.
If you are interested in ADI and would like to learn more about Martensite and Austenite, please contact us.